
When company made money through business, it's nautal for company to think dividend which is share the money company made to each shareholders. Today, let's delve into how company can do dividend in Korea
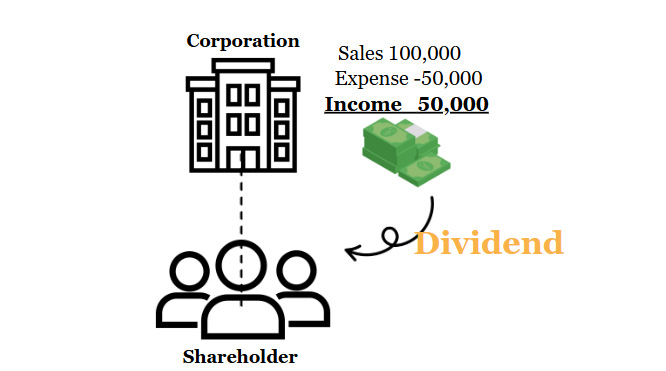
1. When Can a Corporation Pay Dividends?
1)Regular dividend
A regular dividend typically occurs within three months after the end of the business period. For example, if the business period runs from January 1st to December 31st, the corporation should pay dividends by March 31st of the following year.

2)Interim dividend
A corporation can also pay dividends on a specific date set by a resolution of the board of directors, provided the corporation has established this provision in its articles of incorporation.
2. How Much Can a Corporation Pay in Dividends?
1)Calcaultion of dividendable earning
Under Korea’s Commercial Law, there are regulations regarding the amount a corporation can pay as dividends. This is to prevent excessive dividends from negatively impacting the corporation’s financial stability. The formula for distributable earnings is as follows:
| Net asset - The amounts of capital -The total amounts of the capiral reserve and the legal reserve - the amounts of legal reserve that to be accumulated this period - unrealized profits = dividendable earning. |
This ensures that dividends are paid only from legitimate profits, safeguarding the corporation’s financial health.
Let’s simplify the calculation with an example:
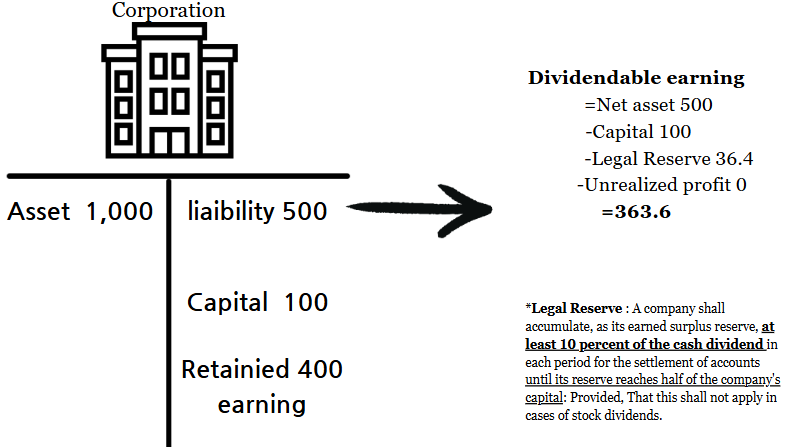
Net assets represent total assets minus total liabilities. To determine the distributable earnings for dividends, follow these steps:
- Start with the net assets.
- Deduct the following:
- Capital amount
- Legal reserve
- Unrealized profit (e.g., income from foreign exchange or similar unrealized gains).
The remaining amount after these deductions is the distributable earnings.
The critical factor in this calculation is the legal reserve. For each dividend period, the legal reserve must be calculated and deducted, ensuring compliance with commercial law.
*If the corporation has already accumulated legal reserves equal to or greater than half of its capital amount, no further deduction for legal reserves is required. This increases the distributable earnings for that period.
2)Equal dividend
When a corporation pays dividends to its shareholders, the amount distributed to each shareholder must align with their ownership proportion (i.e., the percentage of shares they hold in the company).
Unequal dividend distribution is generally not permitted unless under specific circumstances,
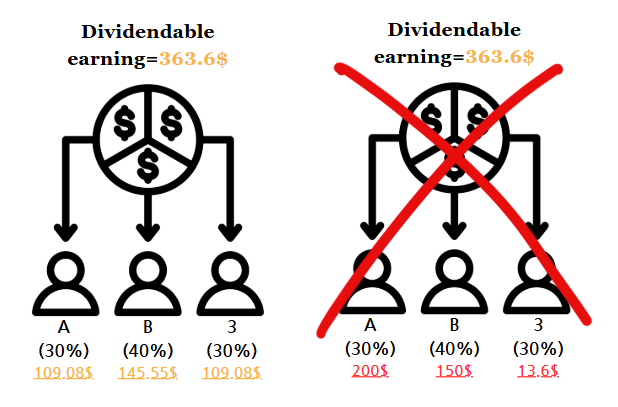
If dividends are distributed unequally the gift taxes or income tax may occur.
3)What should a corporation do for dividend payments?
1)Grant by a resolution of a general meeting of shareholders
When a corporation decides to pay dividends, the process must begin with a resolution passed at the general meeting of shareholders. For small or medium-sized companies with only a few shareholders (or even just one), this may be a formality, but it is still essential to document the decision by preparing minutes of the shareholders' meeting that record the approval of the dividend payment.
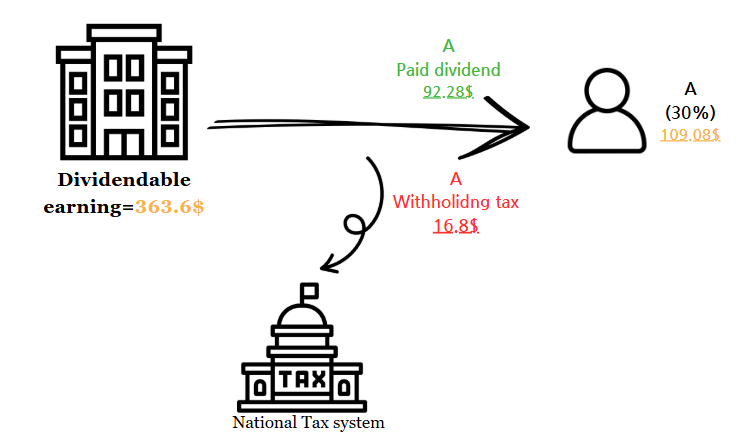
2)Dividend tax withholding
Additionally, the company must handle dividend tax withholding. For individual shareholders, a tax rate of 15.4% (including local tax) applies, and the company must deduct this amount from the dividend before payment and remit it to the tax office. If the shareholder is a non-Korean resident, a reduced tax rate may apply under a tax treaty, and the company should confirm and apply the treaty’s terms. However, if the shareholder is a corporation, no withholding tax is required. These steps ensure compliance with Korean tax and legal requirements for dividend payments.
3)Submission of payment statement
After paying the withholding tax on shareholders' dividends, the company must also submit a payment statement to the tax office. This statement includes details such as the shareholder's name, registration number, the amount of the dividend, and the withheld tax.
G-tax(Seoul, Korea) Tax firm specializing in foreign companies
If you are in search of a reliable English-speaking tax accountant, please don't hesitate to contact us! G-Tax Firm specializes in providing tax services exclusively for foreigners and foreign corporations in Korea. With extensive experience working with international companies, you can trust us for accurate and professional assistance

Thank you for read my article! I hope it helps.
If you want to see more information about Korea tax and accounting, please follow us.
And if you need help for your tax filing or accountung or looking for CPA in Korea, don't hesitate to contace us
G-tax / Certified Tax Accountant / Steven Yang
+82 10 9599 7152 / +82 2 467 2025
steven@g-tax.kr

'Corporate income tax filing' 카테고리의 다른 글
| It's time to get ready for the 2nd VAT return filing. (0) | 2025.01.13 |
|---|---|
| What’s the Difference? Tax Invoice vs. Regular Invoice (0) | 2024.12.16 |
| Foreign Corporations Should Be Careful When Borrowing Money from HQ (Thin Capital Taxation) (0) | 2024.11.28 |
| Donations can cut your company tax. (2) | 2024.10.23 |
| [VAT]How to Prepare for Value Added Tax (VAT) filing (0) | 2024.07.03 |




